

- #Upgrade python to 2.7.9 how to#
- #Upgrade python to 2.7.9 install#
- #Upgrade python to 2.7.9 update#
- #Upgrade python to 2.7.9 software#
#Upgrade python to 2.7.9 install#
usr/local/lib/python2.7.9/bin/pip install virtualenv usr/local/lib/python2.7.9/bin/easy_install pip

SetuptoolsĪs per recommended in Setuptools instructions, we can run easy_install through a wget, like so wget -O - | /usr/local/lib/python2.7.9/bin/python Incomplete scratchpadīut that’s as far as my notes goes for now. You can do that by using fpm (“Fabulous Package Manager”), I am using this technique in a post I published recently about installing a PHP library. Then prepare package through FPM apt-get install -y ruby-dev gcc
#Upgrade python to 2.7.9 how to#
This tutorial shows you how to upgrade Python to version 3.9 on all the major operating systems - Windows, macOS, and Linux. Python 3.9, the latest point release at the time of writing, comes with features such as improved time zone support, dictionary updates, and more flexible decorators. Test if the version works /usr/local/lib/python2.7.9/bin/python -V Every fresh Python release comes with bug fixes and new features. configure -prefix /usr/local/lib/python2.7.9 -enable-ipv6 apt-get install -y gcc-multilib g++-multilib libffi-dev libffi6 libffi6-dbg python-crypto python-mox3 python-pil python-ply libssl-dev zlib1g-dev libbz2-dev libexpat1-dev libbluetooth-dev libgdbm-dev dpkg-dev quilt autotools-dev libreadline-dev libtinfo-dev libncursesw5-dev tk-dev blt-dev libssl-dev zlib1g-dev libbz2-dev libexpat1-dev libbluetooth-dev libsqlite3-dev libgpm2 mime-support netbase net-tools bzip2 Those were the ones I ran last before a successful build on Ubuntu 14.04 LTS, if you aren’t using the same distribution, you might get a different list. If you see procedures that shows you to replace telling you to use update-alternatives to replace python, don’t do it! Go instead learn how to run your own Python version in VirtualEnv. My first though was to upgrade Python to at least 2.7.9, is something. This is why I stopped working on the idea of replacing internally, but instead to configure VirtualEnv to use another version instead. The built in Python in mLinux 3.3.6 is Python 2.7.3 which does not provide TLS 1.2. Since many components within a given Ubuntu version relies on Python, it could break anything else. I realized this while I wanted to upgrade the version and breaking an hard dependency I have on Salt Stack. If you replace internal Python version, other softwares within the OS will have broken dependencies. Why not replacing internal Python version? deb package of Python 2.7.9 and is meant to be used by web applications without touching the system’s python runtime.
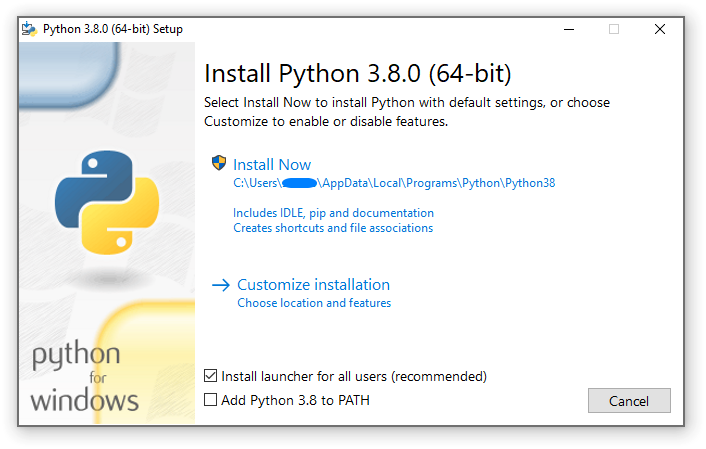
This post attempts to install, and make an installable. Its what virtualenv is all about after all, isn’t it. While I understand that Ubuntu 14.04 will remain using Python 2.7.6 internally, applications we run can be configured to use another python environment. I might rework this article to adjust what’s missing. IMPORTANT This procedure isn’t complete as I had to shift focus elsewhere. And finally if python3 is executed then the chosen version is 3.8.I had this post hanging in my drafts on how I attempted to install a valid Python 2.7.9 runtime environment on Ubuntu 14.04 and make my own. If python2 is executed then the chosen version is 2.7. Which means, if python is executed without specifying any version, python3 will be the chosen version. You will see 3 important links: python python2 and python3 that tell you the versions that your operative system uses.įor example, in my Ubuntu I have python -> python3 These are links in the /usr/bin directory. You can see that by means of the "python links".

#Upgrade python to 2.7.9 software#
But I have also experienced problems trying to run python3.5 software with python3.8. The best example is the incompatibility of python2 and python3 software. How to install Python 3.9 on Linux Mint 20 is explained in this article. Python 3.9 is available from the deadsnakes PPA repository. However, it has gained a lot of popularity in Artificial intelligence and its associated fields like Machine Learning, Deep Learning, etc. The reason was given by If we remove another version of python, we could break all software depending on that version, i.e., we may not be able to run it with the new version. Python is popular and is almost used in every type of computer science project.
#Upgrade python to 2.7.9 update#
In that way, both versions 3.8 and 3.9 would be installed in your Ubuntu.įor instance, in your case, if you do as says sudo apt-get install python3.8, you would not update python2.7 to python3.8, but you would have both python versions installed 2.7 and 3.8. That is, although, you can update python3.8 from your current version (let's say 3.8.2) into the highest available at repository (let's say 3.8.5) by the standard sudo apt-get update, you cannot update from python3.8 to python3.9, neither from python2.7 into python 3.5: you must install the new version parallel to the first one.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
